ad hoc analysis
What is ad hoc analysis?
Ad hoc analysis is a business intelligence (BI) process designed to answer a specific business question by using company data from various sources. A report helps stakeholders assess an event and formulate actionable next steps.
Ad hoc analysis -- also called ad hoc reporting -- in the sphere of BI refers to analysis aimed at answering a specific, immediate question or questions. It takes a quick dive into enterprise data and uses certain tools to create an ad hoc report. Business users do this analysis when needed to address data analysis needs not met by the business's static, regular reporting.
The analysis process begins with BI tools connected to company data sources. The analysis can also be applied to big data from external sources. The latter can be more complex than the former due to the presence of large volumes of structured, unstructured and semistructured data. But the valuable insights in big data can help companies improve customer service, boost revenue or increase efficiency.
IT admins specify the security parameters for user access to the data used for ad hoc analysis. Report models can be built for users to ease report creation. The product is typically a statistical model, analytical report or other type of data summary, presented in the form of charts, tables and cross-tabulations.
Benefits of ad hoc analysis
With ad hoc analysis, business users can extract the immediate insights they need to make better business decisions without having to involve the IT department. Users don't have to wait to get the answers they need, and they can obtain more accurate insights than would be possible with static reporting.
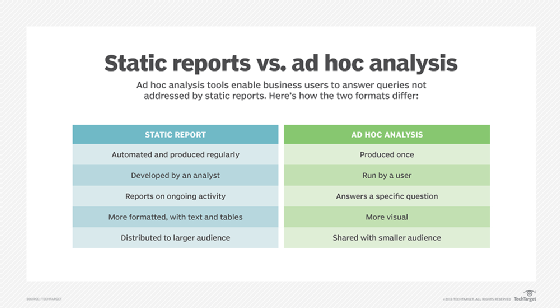
Typically, an ad hoc report is more visual than a standard data report, making it easy for a nontechnical audience to understand and use to gain insight and make decisions. Members of the target audience for the report can also collaborate with each other to uncover trends or patterns in data, get real-time insights, and take faster action to address any uncovered issues. Moreover, the tools are cheaper than older BI tools, allowing organizations to get more value out of their data at a lower cost.
Ad hoc analysis use cases
Ad hoc analysis can be applied to all these real-world areas:
Sales and marketing
Ad hoc analysis and reports can help sales organizations and departments zero in on trends and how they affect sales. For example, they can see how an event influences sales at a particular time or over a specific time frame.
Users can also dig into any aspect of the sales process that is slowing down the sales cycle or hampering sales. Companies can also analyze the effectiveness of their current marketing strategy by considering specific metrics such as cost per acquisition, customer lifetime value, clickthrough rate and more. They can then determine if a new course of action is needed.
Banking and finance
Financial services businesses, including banks, tap into ad hoc data analytics to track and model additional data sources. This helps them better measure and quantify risk, improve cash flow, forecast future performance and boost corporate value.
Healthcare
Healthcare facilities use ad hoc analysis to evaluate blood test results, for example, or track how many patients were admitted to the ER in a given day, week, month or year. This insight can help them improve operational efficiency and lower mortality rates. Ad hoc analysis also promotes greater transparency in the healthcare industry, enabling better decisions around budgeting, staffing and resource allocation.
Government
Government agencies use ad hoc analysis to leverage their massive amounts of data for decision-making on the local, state and federal levels. It helps them better allocate funding, boost productivity and improve resource utilization.
Education
In the education sector, analyzing data can help streamline processes, design more engaging and outcome-oriented programs, and improve program success rates.
Important features of ad hoc reporting tools
Ad hoc analysis tools put the power of analysis in the hands of end users and provide improved intelligence over manual or traditional analysis methods, such as Excel spreadsheets. In addition, the right tools enable users to create targeted reports for on-the-spot analysis, and also help improve processes and generate relevant key performance indicators.
The most important features in ad hoc analysis tools include the following:
Reporting customization
BI tools let users customize reports with preferred charts, graphs, columns or other components. In addition, options such as filters, sliders and conditional formatting can be used to improve reports and provide information that's useful and easy to understand.
Multiple data sources
The ability to pool data from multiple tools and systems provides a rich data set, which then supports analysis and decisions that can improve results.
Basic and advanced features
While ad hoc reporting tools are built for nontechnical users, the best tools offer more advanced features for technical users and users who want granular analysis.
Data visualization capabilities
Data visualization helps users better understand large volumes of data and derive meaning from that data. Designed to simplify data analysis and reporting, these tools support specific data sets and visual data presentation, advancing actionable insights for quicker decision-making.
Sharing options
The best tools allow the sharing of BI among stakeholders and business units to improve collaboration as well as ease decision-making and business improvement.
Other common features of ad hoc reporting tools include drop-down menus and drag-and-drop tools that let untrained business users drill down into the data.
Benefits of ad hoc analysis tools
The best ad hoc analysis tools offer the following benefits:
Customization
Ad hoc analysis tools provide enterprise data analytics across the organization, supporting various niche business needs. They also feature customizable reports to meet users' specific needs. Many tools also provide templates for easier adoption. For more advanced users, Structured Query Language support accommodates a more granular experience and the selection of specific business data to generate reports.
Ease of use
Most data exploration BI tools are user-friendly and built with nontechnical users in mind. The interfaces and dashboards are intuitive and simplify data analysis through a single-use report.
Easy reporting for faster decision-making
Ad hoc reporting tools for self-service BI help users create timely, tailored reports. This speeds up decision-making and response times on business queries.
Reduced IT workload
If the functionality of ad hoc analysis tools is intuitive and sufficiently powerful, business users don't have to rely on IT personnel or developers to write queries and create reports. This allows IT teams to focus on other tasks and saves the business money.
Learn about the top BI tools and how to choose the right one and see how to make better business decisions with financial analytics. Read expert advice on how to start with self-service analytics.





