big data as a service (BDaaS)
What is big data as a service (BDaaS)?
Big data as a service (BDaaS) is the delivery of data platforms and tools by a cloud provider to help organizations process, manage and analyze large data sets so they can generate insights to improve business operations and gain a competitive advantage.
Companies generate immense amounts of unstructured, semistructured and structured data on a regular basis. Big data as a service lets them use third-party providers' data management systems and IT skills to free up organizational resources that would otherwise be devoted to on-premises systems. BDaaS can be dedicated systems and software running in the cloud or a contract for a managed service that a cloud vendor hosts and operates.
BDaaS is a form of cloud computing, similar to software as a service, platform as a service and infrastructure as a service. In addition to using the data processing frameworks and associated tools at the core of these cloud services, BDaaS relies on cloud storage to maintain data sets and provide the user organization with access to them.
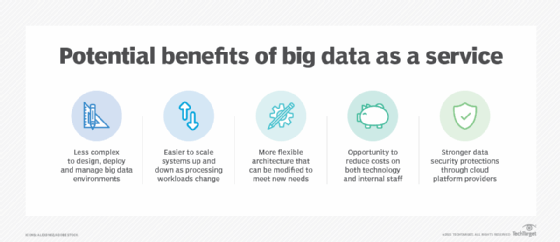
Benefits of big data as a service
In the past, large enterprises often installed big data systems in on-premises data centers. These systems combined various open source technologies to fit an organization's particular big data applications and use case needs. More recently, deployments have shifted to the cloud because of its potential advantages. The following are some of the benefits of big data as a service:
- Reduced complexity. Because of their customized nature, big data projects and environments are complicated to design, deploy and manage. Using cloud infrastructure and managed services eliminates much of the hands-on work that organizations need to do and simplifies the process.
- Easier scalability. In many environments, data processing workloads aren't consistent. For example, big data analytics applications often run intermittently or just once. BDaaS makes it easy to scale up systems when processing needs increase and to scale them down again after jobs are completed.
- Increased flexibility. BDaaS users can easily add or remove platforms, technologies and tools to meet evolving data-driven business requirements. This isn't as easy to do in on-premises big data architectures.
- Potential cost savings. Using the cloud, businesses don't have to buy new hardware and software and hire workers with big data management skills. As a result, cost savings are possible. But pay-as-you-go cloud services must be monitored to prevent unnecessary processing expenses from driving up costs.
- Stronger security. Concerns about data security kept many organizations from adopting the cloud at first, particularly in regulated industries. In many cases, though, cloud vendors and service providers have invested in better security protections than individual companies are generally able to.
Challenges of big data as a service
Despite myriad benefits for enterprises, BDaaS isn't foolproof and if these services aren't managed correctly, they can create headaches. Some of the potential drawbacks to be aware of include the following:
- Data Privacy. These services aren't immune to today's advanced cyberattacks. Sensitive or personally identifiable information can be compromised if users aren't careful about data privacy and security.
- Data governance and regulatory compliance. BDaaS providers don't offer built-in data governance practices that ensure responsible and ethical data use, so the burden is on user organizations to find other ways to ensure data governance. This can be a challenge, especially with unstructured data. Also, ensuring data use is compliant with regulations and legal frameworks is a task that organizations using BDaaS services must tackle themselves.
- Cost management burdens. Using cloud-based BDaaS services means organizations can avoid costly infrastructure purchases, however, organizations must manage how they use these services or unnecessary costs can accumulate over time. To prevent this, they must control spending and optimize their use of these resources.
- Management complexities. This is especially true of larger organizations where BDaaS capabilities are meant to span all departments. Large volumes of data used and stored across an entire organization can be difficult to manage. Therefore, data scientists and business leaders should communicate a game plan to manage data effectively to everyone they employ.
Key elements of BDaaS offerings
The big three cloud platform vendors each offer big data technology bundles and services: Amazon EMR from Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Dataproc and Microsoft's Azure HDInsight. A sampling of other big-data as-a-service vendors includes Cloudera, Databricks, HPE, IBM, Oracle and Qubole.
The competing BDaaS platforms provide different combinations of open source big data software. Common core technologies include the Hadoop distributed processing framework, Spark processing engine, Hive data warehouse software and Python, R and Scala programming languages. The following are examples of tools that are often included as standard or optional components:
- HBase, Hadoop's companion database.
- Flink, Kafka and other real-time stream processing engines.
- Presto, a rival SQL query engine to Hive.
- The Tez application framework.
- Analytical tools such as Jupyter Notebook, Mahout, Pig and Zeppelin.
- Oozie workflow scheduler.
- ZooKeeper cluster configuration service.
Data can be stored in the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), which is one of Hadoop's core components, or in cloud-based object storage services like Amazon Simple Storage Service, Google Cloud Storage and Microsoft Azure Blob Storage. BDaaS platforms can also connect to data warehouse and data lake environments, such as Azure Data Lake Storage, Delta Lake, Iceberg and Snowflake.
BDaaS market trends
While the BDaaS market is primarily focused on public cloud deployments, users can install the AWS, Google and Microsoft platforms in their own data centers and other on-premises facilities. Added support is available to run the big data services on each vendor's hybrid cloud platform -- AWS Outposts, Google Anthos and Azure Stack, respectively. Using those technologies, organizations can set up private clouds or mix public cloud and in-house systems in their big data environments.
All three vendors have tied their BDaaS platforms to Kubernetes services. These enable organizations to use the popular container management framework to create containerized big data applications, which can help simplify deployments, streamline infrastructure management and optimize the use of system resources.
AWS, Google and other BDaaS vendors are now emphasizing Spark and other technologies over Hadoop, which was initially at the center of their offerings and the big data ecosystem. That reflects a broader decline in Hadoop's standing vs. Spark as a batch processing engine, although Hadoop's YARN cluster resource management software and HDFS continue to be widely used.
Big data storage is an important part of big data management, but large volumes of data must be culled from sources first. Learn about how big data collection works.





