BIOS password
What is a BIOS password?
A BIOS password is authentication information that's sometimes required to log into a computer's basic input/output system (BIOS) settings before the computer boots up.
BIOS is the program a computer's microprocessor uses to control the computer's initial boot sequence when it's powered on. BIOS also manages the data flow between the computer's operating system (OS) and attached devices, such as a keyboard, mouse or hard disk.
A BIOS password helps prevent unauthorized users from making changes to the computer's hardware and software settings. But a BIOS password can also be a liability: If the computer owner forgets their password or an employee turns in their machine without disclosing their BIOS password, the computer won't boot up.
BIOS is accessed from a cold boot of a user's desktop or laptop device. The process of accessing BIOS differs by computer, but after a boot, the manufacturer's logo appears, followed by on-screen prompts, including the option to press a key to open settings. Upon selecting the BIOS settings, the computer presents the user with a password -- provided the password is already set up. If the password isn't set up, users can set their own BIOS password. Password settings can be located by selecting the Security tab.
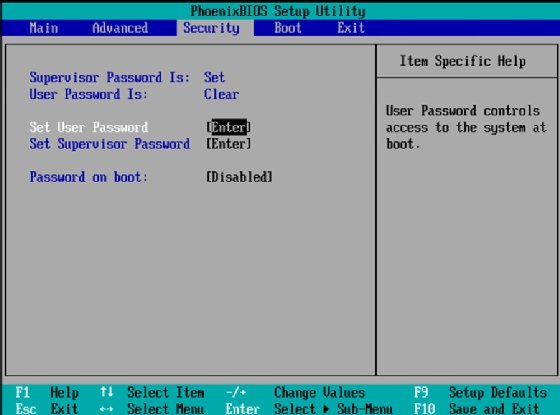
BIOS also lets users set up a separate system password that they must input before the OS can boot up. This is a separate password from the BIOS password, which is needed to access the BIOS settings.
How to find your BIOS password
The BIOS password prompt is presented to users upon a cold boot of the device and when users follow their machine's prompts to open BIOS settings.
If administrators need to remove or change a BIOS password on Windows 10, they should choose the option to set the password. Otherwise, leaving the field blank effectively removes the requirement for a password.
If a user forgets or doesn't know their BIOS password, the vendor might be able to reset the password. Resets typically involve the use of backdoor BIOS passwords. These are master BIOS reset passwords created by the BIOS manufacturer that work no matter what password the user has set up.
However, if the device's vendor can't help, there are still a few options for bypassing the password, including the following:
- Remove and reinsert the complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) battery. In older devices, the BIOS password is stored in CMOS memory. In some computers, a small battery attached to the motherboard maintains the memory when the computer is off. User-created passwords can sometimes be cleared by removing the CMOS battery, waiting a few minutes, then reinstalling it. However, many new laptops store their BIOS passwords in a way that doesn't require continuous power, preventing this method from working.
- Use the BIOS reset jumper method. Some manufacturers provide a jumper plug that lets users bypass the BIOS password using password jumper pins. The location of these, if included, differs per manufacturer.
- Short the electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM) chip pins. Some older BIOS-locked devices can be accessed by shorting specific EEPROM chip pins with a screwdriver. This vulnerability was discovered on a few Lenovo ThinkPad laptop models and might work on other devices that store passwords on EEPROM chips.
Other possible ways to bypass the BIOS password include the following:
- Use special third-party BIOS password cracking software such as BIOS-pw.
- Overload the keyboard buffer.
- Contact a professional service.
After the BIOS is reset, previously made setting changes -- such as the clock or boot order -- must be made again.
Learn more about how to change the BIOS password on Windows 10.



