cloud access security broker (CASB)
What is a cloud access security broker (CASB)?
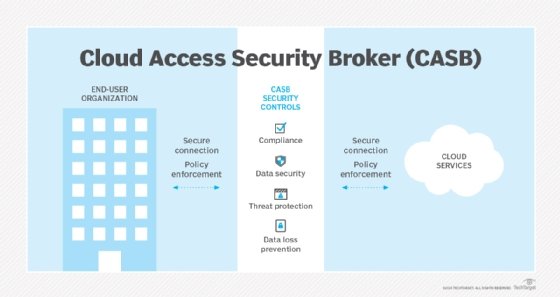
A cloud access security broker (CASB) is a software tool or service that sits between an organization's on-premises infrastructure and a cloud provider's infrastructure. A CASB tool provides a unified and consistent method for an organization to access cloud resources.
CASBs are designed to combine and enforce an organization's security policies when accessing cloud-based resources. They help prevent potential threats that can occur when an organization adds cloud-based networking to the IT infrastructure.
Cloud access security brokers combine security policies such as authentication, credential mapping, encryption, logging and malware detection. A CASB tool sits between on-premises infrastructure and the cloud so that any traffic sent to the cloud can first have security policies enforced.
CASBs typically offer the following:
- Firewalls to identify malware and prevent it from entering the enterprise network.
- Authentication to check users' credentials and ensure they only access appropriate company resources.
- Web application firewalls to thwart malware designed to breach security at the application level rather than at the network level.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) to ensure users cannot transmit sensitive information outside the corporation.
CASBs are available as both on-premises and cloud-based software, as well as software as a service (SaaS).
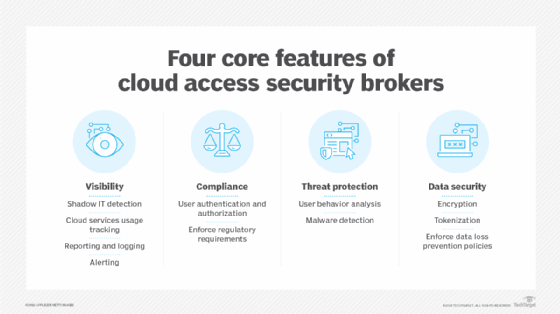
4 pillars of CASB
A CASB acts as a gatekeeper, allowing organizations to extend the reach of their security policies beyond their own infrastructure.
The core components of a CASB include the following:
- Visibility. Visibility is an important aspect to help create a secure environment. In a cloud environment, organizations typically have limited visibility and insight into the cloud provider's underlying infrastructure. CASBs improve visibility for cloud usage with access logs that provide insights on corporate cloud infrastructure and attempted attacks. CASBs can also help detect instances of shadow IT.
- Compliance. Different regional regulations -- such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act or the General Data Protection Regulation -- can apply to organizations, meaning an organization must make sure its cloud provider complies with any regulations that might apply to the organization and its customers. CASBs define strict access controls to help comply with data regulations.
- Data security. CASBs provide data security through access management and DLP processes that help secure an organization's cloud-based data.
- Threat protection. Employees might unintentionally introduce malware-based threats to cloud-based services. A CASB tool can detect and prevent potential threats. Any file upload, for example, can be inspected before it is sent to the cloud.
How does a CASB work?
CASBs work by ensuring network traffic between on-premises devices and the cloud provider complies with an organization's security policies.
The value of cloud access security brokers stems from their ability to give insight into cloud application use across cloud platforms and identify unsanctioned use. This is especially important in regulated industries.
This article is part of
What is cloud security management? Guide and best practices
CASBs work in a discovery, classification and remediation process. The discovery process identifies in-use cloud applications, the classification process assesses each application and creates a risk factor, and the remediation process identifies and remediates detected threats based on the organization's security policy.
CASBs use auto-discovery to identify cloud applications in use and identify high-risk applications, high-risk users and other key risk factors. Cloud access security brokers enforce a number of different security access controls, including encryption and device profiling. They can also provide other services such as credential mapping when single sign-on is not available.
Use cases for CASBs
CASB tools have evolved to include, or work alongside, other IT security services -- though some vendors still offer standalone tools. CASBs are particularly useful in organizations with shadow IT operations or liberal security policies that allow operating units to procure and manage their own cloud resources.
Potential uses for CASB tools include the following:
- Data security. CASBs collect and configure granular access to data. DLP features also enable users to protect sensitive data that transfers to or from a cloud service.
- Network security. CASBs offer firewalls and web application firewalls.
- Protection against malware. CASBs can protect against cloud-based malware threats that users might accidentally introduce to the environment.
- Monitoring. CASBs can continuously monitor users by activity, application, cloud service usage and identity. CASBs can also be used for budgeting purposes.
- Compliance. Organizations can use CASBs to assess compliance with security, regulatory and legal standards.
- Cloud application usage tracking. CASBs can provide a way to view cloud application usage, making it easier to identify abuse and usage patterns.
- User behavior analytics. Usage tracking serves as a foundation for more sophisticated behavior tracking, as the same data is subjected to more detailed analysis.
Cloud access security broker vendors and resources
Vendors and tools in the cloud access security space include the following:
- Skyhigh Security's Skyhigh CASB.
- Broadcom's CloudSOC CASB.
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps.
- Fortinet's FortiCASB SaaS.
- Citrix Secure Workspace Access.
Microsoft also includes CASB functionality in its base Azure security services at no extra charge.
To meet the needs of infrastructure-as-a-service and platform-as-a-service users, CASB vendors have also added or expanded functionality for security tasks, such as the following:
- Single sign-on. Allows employees to enter their credentials one time and access a number of applications.
- Encryption. Encrypts information from the moment it's created until it's sitting at rest in the cloud.
- Compliance reporting tools. Ensure the company's security systems comply with corporate policies and government regulations.
- User behavior analytics. Identifies aberrant behavior that could indicate an attack or data breach.
These features help enable tougher security functions. Learn more about why CASB tools are critical to cloud security.





