taxonomy
What is taxonomy?
Taxonomy is the science of classification according to a predetermined system, with the resulting catalog used to provide a conceptual framework for discussion, analysis or information retrieval. The word is rooted in two Greek words: taxis meaning arrangement or division, and nomos meaning law.
Taxonomy is a methodology that involves systematically classifying elements in a defined hierarchical form. The concept is common in life sciences, botany and zoology, where taxonomies are used to classify plants and animals.

In these areas, taxonomists identify, describe and arrange different plant or animal species in hierarchical groups. These groups include both superior and subordinate elements. Creating a taxonomy helps to classify living organisms based on their characteristics, and it simplifies information retrieval and cross-referencing for zoologists and botanists.
One of the best-known and most commonly used taxonomies in biology is the one devised by the Swedish scientist Carl Linnaeus. In the Linnean system of binomial nomenclature, every organism is classified based on its genus and its species. Since two terms are used -- both Latinized -- the nomenclature is known as a binomial one. For example, the American robin is classified in the Linnean system as Turdus migratorius, while modern humans are known as Homo sapiens.
In addition to biology, taxonomies are also created in other real-world areas, such as computing.
Taxonomy in computing and web design
For example, in web portal design, taxonomies are used to describe categories and subcategories of topics found on the website. The categorization of words on TechTarget Editorial's WhatIs site is similar to any web portal taxonomy.
In website design, a taxonomy provides a systematic way to classify the various content elements that will go into the site. It shows how things are -- or will be -- organized on the site and classifies them as pages, sections or categories, for example. The elements are organized in a logical manner to simplify navigation for the site's users, allowing them to understand its setup and purpose.
A website's taxonomic structure will organize its content as well as its URLs. The URL structure refers to the way URLs, including domains and subdomains, are organized to reflect the content in each webpage. Typically, the structure includes all the directories and subdirectories within the main domain.
As the content on each page gets more specific, subdirectories and URL slugs change, while the main domain remains the same. Thus, the main domain of TechTarget will always be www.techtarget.com. However, for the page titled "Taxonomy," the URL will change to www.techtarget.com/searchcontentmanagement/definition/taxonomy to reflect this page's unique content.
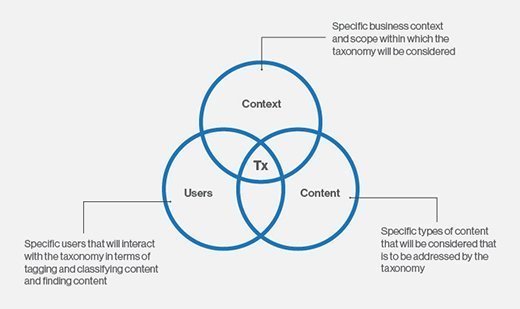
Taxonomies for digital content
Digital content is expanding at a rapid pace. To maintain its usability and usefulness, it must be organized into a proper structure with multiple interrelated components. A taxonomy helps create this structure by grouping information into logical chunks. The taxonomy can include metadata, which is data that describes the data stored in the taxonomy. That structure and metadata make it easy to understand what each piece of content is about, simplifying content management retrieval and use.
Recently, technologies such as natural language processing (NLP) have evolved. NLP applications when combined with content taxonomies are useful to tag, classify, organize and even summarize natural language text. Programs with taxonomic capabilities -- programmatic taxonomy -- provide hierarchical context to digital content so that it becomes discoverable, not only for human users, but also for machines.
Programmatic taxonomy tools also automate document classification, information extraction, and speech-to-text conversion by identifying keywords and tagging niche terms. These capabilities are particularly useful in fields where the content generated is often complex, jargony and impossible for traditional speech-to-text applications to understand. Examples include medical and legal documents.
Qualities of a good taxonomy
A good taxonomic classification takes into account the importance of separating elements of a group, or taxon, into subgroups, or taxa, that are mutually exclusive and unambiguous, and taken together include all known possibilities. These possibilities should help disseminate knowledge about the topic of the taxonomy.
The taxonomy itself should be simple, easy to remember and easy to use. It should follow a hierarchical format and use a uniform and easily understood nomenclature to enable information understanding and retrieval.
Regardless of the subject or domain, the taxonomy should be based on rules that help classify and categorize the objects or elements in that domain. Moreover, the rules should be easy to understand and should be implemented consistently to maintain the taxonomy's rigor and integrity.
Ideally, a taxonomy should be rigorous enough to ensure all newly discovered objects can fit into a category. Each object can inherit the properties of its superior class -- the class above it -- and also have its own additional or unique properties.
Benefits of taxonomies in the digital age
Any digital application that generates or uses content can benefit from the content structure and nomenclature provided by a taxonomy. Digital taxonomies group, categorize and organize content so that it becomes easier for a user or application to find information. A systematic hierarchical taxonomy also does the following:
- Helps users to find related information and correlations.
- Simplifies navigation, thus improving the overall user experience.
- Reduces the time and effort needed to track, manage or update content.
- Improves content quality and usefulness.
- Organizes content metadata and improves its quality.
- Enables content owners to govern and protect data assets.



