
conversational AI (conversational artificial intelligence)
What is conversational AI (conversational artificial intelligence)?
Conversational AI (conversational artificial intelligence) is a type of AI that enables computers to understand, process and generate human language.
Conversational AI has primarily taken the form of advanced chatbots. They're different from conventional chatbots, which are predicated on simple software programmed for limited capabilities. Conversational chatbots combine different forms of AI for more advanced capabilities. The technologies used in AI chatbots can also be used to enhance conventional voice assistants and virtual agents. The technologies behind conversational AI platforms are nascent yet rapidly improving and expanding.
A conversational AI chatbot can answer frequently asked questions (FAQs), troubleshoot issues and even make small talk -- contrary to the more limited capabilities of a static chatbot with narrow functionality. Static chatbots are typically featured on a company website and limited to textual interactions. In contrast, conversational AI interactions are meant to be accessed and conducted via various mediums, including audio, video and text.
How does conversational AI work?
Conversational AI combines natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) processes with conventional, static forms of interactive technology, such as chatbots. This combination is used to respond to users through interactions that mimic those with typical human agents. Static chatbots are rules-based, and their conversation flows are based on sets of predefined answers meant to guide users through specific information. A conversational AI model, on the other hand, uses NLP to analyze and interpret the user's human speech for meaning and ML to learn new information for future interactions.
This article is part of
A guide to artificial intelligence in the enterprise
NLP processes large amounts of unstructured human language data and creates a structured data format through computational linguistics and ML so machines can understand the information to make decisions and produce responses. An ML algorithm must fully grasp a sentence and the function of each word in it. Methods like part-of-speech tagging are used to ensure the input text is understood and processed correctly.
Regardless of the scope and purpose of a conversational AI tool, the process by which end users interact with it and vice versa typically includes the following four steps:
- Input generation and reception. End users create input, such as a query, and the tool receives it. It can be a textual input or a voice prompt that requires voice recognition technology to convert it into machine-readable text.
- Input synthesis and analysis. To understand the meaning of user input, the tool relies on natural language understanding (NLU) to successfully process and analyze it.
- Output generation. Using its key components, particularly the dialogue design, training data and ML algorithms its developers used to prepare it, the tool generates output. This output can range from simple answers to complex responses depending on what the user's input requires.
- Output delivery. The requested output is delivered back to the user.
What are some examples and use cases of conversational AI?
Organizations can build and apply different types of conversational AI tools for various practical uses. Examples include the following:
- All-encompassing, subscription-based chatbots. These advanced chatbots generate text to answer user queries on a range of topics. Foremost among these tools is OpenAI's ChatGPT. OpenAI requires users to present login information to interact with the application, and paid subscriptions are available.
- AI-powered search engine assistants. A search tool with AI functionality can quickly produce search results that best match a user's query. The most prominent examples are Google Bard and Microsoft's Copilot in Bing.
- Conversational business intelligence (BI) apps. Conversational BI combines conversational AI with data analytics capabilities -- in a sense, letting users talk to these applications and receive outputs in the form of data visualizations and explanations. A conversational BI application is integrated with a database or data warehouse from which it retrieves data needed for analysis and visualization.
- Customer service chatbots. The most well-known chatbots and virtual assistants are on company websites, offering limited responses to customer inquiries and some predetermined functionality. Virtual assistant platform vendors offer services to help businesses better engage their customers. IBM Watsonx Assistant is one prominent example.
Processes and components of conversational AI models
NLP technology is required to analyze human speech or text, and ML algorithms are needed to synthesize and learn new information. Data and dialogue design are two other components required within conversational AI. Developers use both training data and fine-tuning techniques to tailor a system to suit an organization's needs.
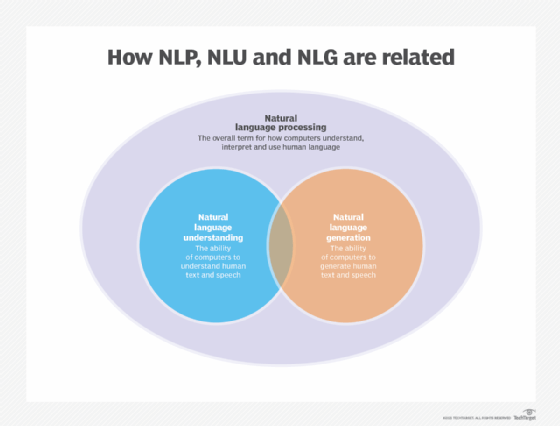
Additionally, two subareas of NLP play a crucial role in conversational AI:
- NLU is what enables a machine or application to process the language data in terms of context, intent, syntax and semantics, as well as ultimately determine the user's intended meaning.
- Natural language generation (NLG) is the process by which the machine generates text in human-readable languages, also called natural languages, based on all the input it is given. The goal of an NLG system is to explain the AI's structured data to humans.
What are the benefits of conversational AI?
Conversational AI is expanding and offering benefits to many different types of businesses. Organizations across different industries, including the following, can apply conversational AI to a range of scenarios and reap the benefits:
- Healthcare. Conversational AI can help patients describe their conditions online through a series of questions meant to circumvent wait times.
- Retail. When customer service representatives aren't available, AI-powered chatbots are able to meet customers' demands on a 24/7 basis, even during holidays. Historically, call centers and in-person visits were the only way to interact with customers. Now, customer support is no longer limited to office hours because AI chatbots are available through various mediums and channels, including email and websites.
- Banking. Banks use AI chatbots to handle complex requests in a manner that conventional chatbots struggle with. When dealing with customers' finances, it's especially important to eliminate common human errors and deliver precise and accurate responses or solutions to address concerns.
- Internet of things. Common household devices have conversational AI capabilities via interfaces such as Amazon's Alexa and Apple's Siri. Conversational AI agents are also integrated in smart home devices.
- Human resources (HR). Conversational AI can automate the time-consuming HR process of sifting through candidate credentials manually in the job recruitment process.
What are the challenges of conversational AI?
Developers and their organizations must consider some common challenges with conversational AI systems, such as the following:
- Language translation. Many conversational AI models have thus far been trained primarily in English and can't interact with non-English speakers in their native languages. Multilingual proprietary chatbots are an option for customer service at companies with global operations.
- Security. Companies that conduct customer interactions via AI chatbots must have security measures in place to process and store the transmitted data.
- Difficulty interpreting certain words and contexts. Conversational AI can be thrown off by slang, jargon and regional dialects, which are all examples of the changing nature of human languages. Developers are starting to train the technology to address such challenges.
For more on artificial intelligence in the enterprise
Artificial intelligence vs. human intelligence: How are they different?
AI vs. machine learning vs. deep learning: Key differences
Main types of artificial intelligence: Explained
What is trustworthy AI and why is it important?
The future of AI: What to expect
AI regulation: What businesses need to know
Steps to achieve AI implementation in your business
How businesses can measure AI success with KPIs
Conversational AI vs. generative AI
Conversational and generative AI are two distinct concepts that are used for different purposes. However, there is some overlap. For example, ChatGPT is a generative AI tool that can generate journalistic articles, images, songs, poems and the like. It's also a highly advanced chatbot that can be used for customer service.
Conversational AI
Conversational AI is focused on NLP- and ML-driven conversations with end users. It's frequently used to get information or answers to questions from an organization without waiting for a contact center service rep. These types of requests often require an open-ended conversation. Hence, users need a conversational AI tool.
Training data provided to conversational AI models differs from that used with generative AI ones. Conversational AI's training data could include human dialogue so the model better understands the flow of typical human conversation. This ensures it recognizes the various types of inputs it's given, whether they are text-based or verbally spoken.
Generative AI
Generative AI is focused on the generation of content, including text, images, videos and audio. If a marketing team wants to generate a compelling image for an advertisement, the team could turn to a generative AI tool for a one-way interaction resulting in a generated image.
The training process for generative AI models uses neural networks to identify patterns within their training data. This analysis, along with human guidance, helps generative models learn to improve the quality of the content they generate. Ultimately, their goal is to produce outputs that are accurate and realistic.
How to create conversational AI
Before developers start working on building a conversational AI application, a planning and creation process is required. This process should assess the scope and conversation structure that a tool is expected to follow when users interact with it. The steps involved include the following:
- Compile potential inputs from end users. Assembling a list of inputs expected from end users during interactions is the first step in this process. An existing FAQ list or data collected from previous customer interactions is enough to move forward.
- Craft scope and purpose with sample inputs. From the potential user inputs gathered in the first step, it's possible to glean what users are probably looking for in their interactions with the conversational AI tool. It's important to consider the manner or phrasing users might use when making requests. Using all this information to define the scope and purpose of the tool makes it comprehensive enough to handle various user inputs and respond to the different ways requests are made.
- Define goals. With enough data and sample inputs, specific requirements and goals can be identified for the tool. These lay the groundwork for the design of full dialogue or conversation flows with future intended users.
- Design and test a prototype. Once all requirements are identified, a prototype model is designed and built. This approach lets developers determine if what they're thinking works, and they can also identify possible issues.
- Test the model with end users. Human developers guide and train the prototype tool through the potential interactions and scenarios it will have with users. The result should be a conversational AI tool that can interact smoothly with humans and answer questions with appropriate responses.
- Reinforcement learning. Reinforcement learning as part of the training process conditions a model to produce more accurate outputs over time. This method rewards the model for producing desired outputs and steers it away from erroneous ones. This optimizes model performance.
Conversational AI tools can deliver good customer service experiences, but they also come with some problems. Learn more about the inherent risks associated with using ChatGPT and other AI tools for these tasks, including false information, biases and security concerns.




