data loss
What is data loss?
Data loss is the intentional or unintentional destruction of information. Data loss can be caused by people and/or processes from within or outside of an organization.
Data loss is similar to a data breach, in that data is compromised. However, in a data breach, data is usually unharmed but in the wrong hands. Data loss can occur in a data breach if the data itself is destroyed.
There are many causes of data loss, and those can differ by industry. Some organizations might be more concerned about outside attacks, while others are primarily worried about vulnerability to internal human error. Data loss can occur during standard IT procedures such as migration, or through malicious attacks via ransomware or other malware.
The impact of data loss might also differ based on who the data belongs to. Along with affecting an organization's internal data, the loss of an outside party's confidential data can jeopardize a business's legal compliance.
How data loss occurs
Common unintentional causes of data loss include hardware malfunction, software corruption, human error and natural disasters. Data can also be lost during migrations and in power outages or improper shutdowns of systems.
Hardware malfunction is the most common cause of lost data. A hard drive can crash due to mishandling, overheating, mechanical issues or simply the passage of time. Proper hard drive maintenance can help prevent data loss, and being mindful of a drive's lifespan enables users to prepare for the drive's replacement.
Software corruption is another common cause of data loss and can take place when systems are improperly shut down. These shutdowns can usually be attributed to power outages or human error, so it falls on the organization to prepare for these incidents and ensure the proper shutting down of systems.
Natural disasters can cause data loss through all the above, be it damage to hardware or causing systems to fail without data being backed up. Disaster recovery planning and frequent backups are the best strategies for preventing this type of data loss.
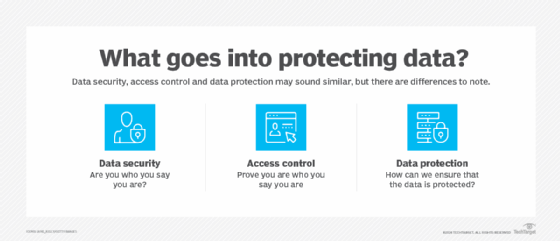
Computer viruses such as malware can cause intentional data loss. To help prevent this, organizations must keep antivirus software up to date and ensure that employees are aware of potential malware threats.
Hackers can also cause intentional data loss from within or outside of an organization. These incidents require different protection methods, particularly regarding access. To prevent intentional data destruction from recent or current employees, a company should limit access to confidential or sensitive data to necessary personnel only. Controlling or restricting access can also aid in preventing loss via hackers or even human error, where an employee may unintentionally erase data without knowing the severity of the action.
Impact of data loss
Preventing data loss can be an expensive process, requiring the purchase of software or other backup and data protection products or services. While the costs of these services can be high, thorough protection against data loss is usually worth it in the long run, especially when compared to potential costs down the line.
In the case of major data loss, business continuity and day-to-day functions can be severely affected, tacking on additional costs. Company time and resources will often need to be diverted to address data loss and recover the most recent copy of lost data, so other business functions may be affected.
An organization's reputation can also suffer following data loss. Customers need to be informed of the loss, and those customers might take their business elsewhere. Giving personal, sensitive data to another company takes trust, and the loss of data can make an organization look unreliable. Rebuilding these relationships takes significant time and company resources.
Data loss prevention strategies
Data loss prevention (DLP) can take the form of a strategy or a product that aims to mitigate or prevent data loss in case of an incident. DLP strategies tend to target the sharing of sensitive data outside of the corporate network, while software products control this aspect by limiting what users can transfer or share.
The end goal of DLP is to protect confidential and sensitive data from unauthorized users who could mishandle or maliciously share it. Whether in response to insider threats or the need to conform to outside data protection regulations, having a data loss prevention plan is becoming an important part of a modern backup and data protection strategy.
Legal ramifications
When an organization is responsible for protecting someone else's data, it also takes on the responsibility to keep those people or organizations informed of the status of their data. In the United States, each state has enacted legislation requiring both private and government organizations to inform relevant parties of a breach or loss of their data.
Enacted in May 2018, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation addresses notifying affected parties of a data breach or loss. In Article 33 of the GDPR, there is a mandatory 72-hour countdown for organizations to gather information and report on data breaches to the regulator, as well as the impacted individuals involved in the breach. Along with notification, the organization must draft a plan to recover the data within those 72 hours.
While the GDPR is an EU regulation, it applies to any organization that has the data of EU citizens. Because of this, any organization globally that collects this type of data is liable for data loss and subject to the GDPR rules.
Recovery after data loss
Backups are key to recovering from data loss, ensuring that an organization has at least one additional, recent copy of vital data. To ensure that backups are safe, off-site backups are recommended to protect them from threats that take place in or around the data center. Copies kept out of reach may be more difficult to access later on but provide an extra layer of protection.
Cloud backups can be accessed with relative ease following data loss, but organizations should vet a cloud provider to ensure that data will be protected and retrievable. Performing frequent backup and recovery tests can help to make sure that data is properly backed up and formatted and can be accessed as quickly as necessary.
Having antivirus software in place is the best protection against malicious attackers, so it should be updated frequently. For the more physical threats such as natural disasters or fire, computers and hard drives should be kept in a clean, dry and secure location. Organizations should also monitor employee access to files and equipment. Proper training regarding confidentiality and the sharing of data can help prevent loss by human error.