How to develop a business process in 8 steps
Well-designed business processes help organizations achieve their goals faster, but they require planning and effort. Follow these steps to develop processes that deliver value.
Business processes are core to organizations. They represent the tasks, activities and overall flow of work that achieves the business's core mission and objectives.
Well-defined and documented business processes help organizations achieve their goals faster, lower costs, reduce errors and free up more time for employees to focus on higher-value tasks. Implementing defined business processes not only helps streamline and optimize an organization's operations but also sets the foundation for continuous process improvement and efficiency.
Developing a business process requires planning
Creating a high-quality, valuable business process takes time and effort to plan, develop and implement. Setting the structured sequences of activities, tasks, actions and steps performed by team members of successful business processes can be challenging.
The steps are generally followed in a specific order to achieve consistent and desired outcomes. Each task in a business process is then broken down into smaller subprocesses and tasks, defined for their operation and flow, and documented.
Business processes also vary in duration, complexity and number of steps depending on the nature of the task. Fundamentally, a business process is supposed to represent a core operation for the business to accomplish a specific outcome. There are two ways to determine the steps in a business process. You can start from how the process currently works ("as is") or how you want the process to work ("should be"). For an as-is process, the steps focus on identifying how the process works currently as well as the tasks and steps currently employed. For a should-be process, the steps focus on identifying what the tasks need to be in the process and how they will be coordinated to achieve an outcome.
To have an effective business process, organizations need to identify which tasks are the most important for the desired outcome, ensuring accountability, streamlining communication channels and setting standards for how the business performs its activities.
In addition, business processes are never a "set it and forget it" project, so it's important for managers involved in process management to understand that iteration of the process is also very important. Core business processes that add value to the organization require continuous process improvement, documentation, testing and evaluation.
Here are eight basic steps to developing a business process.
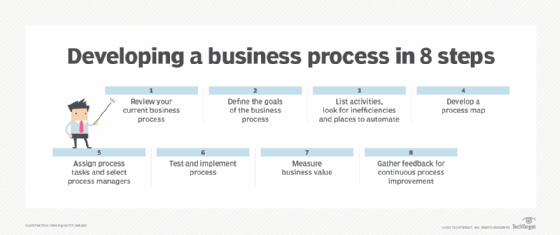
1. Review the current business process
It's helpful to start by reviewing what you are currently doing in your business process. Look for redundancies and low-value activities. Bring in stakeholders and other key people running the day to day of the process to evaluate what is working and what can be improved. Make sure to also factor in what work and tasks stakeholders actually enjoy doing and what they would like to see automated, changed or eliminated.
2. Start by defining the goals of the business process
When creating business processes, it's important to do so with the end in mind. Organizations need to figure out what the goals are for a specific business process, and then work their way from the goals to the subprocesses and tasks. It's important to focus on efficiency, ROI, performance improvement and timesaving measures at this stage. Set clear, measurable goals for the process. You'll want to include the specific and time-sensitive goals your stakeholders want to see come out of the process, such as "double sales in two years."
3. List activities and look for inefficiencies and places to automate
The tasks in a process can be performed in a variety of ways: by internal workers; by external, outsourced workers; by machines; or by a combination of workflow automation and human effort. Organizations that map their processes have an opportunity to identify where and how to automate, optimize and improve current processes.
Start by listing out all current and potential activities of a process. Listing out each activity's tasks will help with future task prioritization of process steps. Consider relationships between activities, causes and effects of activities, and points where each activity fits into the process. Then figure out which activities can be automated, optimized, streamlined or eliminated. Business process automation technologies provide a way to increase efficiency in processes with repetitive tasks.
4. Develop a process map
After figuring out all the required activities in a process, you'll next want to map out your process in a sequential, easy-to-understand manner. Start with the first step needed in your process and plan out how best to arrive at your desired result. Determine where handoffs between departments occur, which processes need to happen sequentially and which can run in parallel. Come up with a timeline, and determine the costs for each task and the process as a whole.
Business process modeling approaches provide a useful method to help stakeholders see the process in a visual manner, which can further help you spot redundancies, bottlenecks and other issues you might have missed when defining the process. Approaches such as using a flow chart or other visual methods can provide an easy way to understand the progression of necessary actions to reach a specific outcome.
5. Assign process tasks and management
Once a process has been defined and mapped, you'll want to assign each team member or department to specific activities and tasks. Some of these assignments will be obvious and easy to do. But other tasks might require more thought to determine the most optimal person or department responsible.
Assign managers for these tasks for supervision and ownership, including supervision over any tasks determined to be automated. Just because it's not being done by a human doesn't mean it can run on its own without any human in the loop. Make sure to clearly state expectations and timelines for tasks, get involvement and input from managers in this process, and continue to track and measure goals.
6. Test and implement the process
Process definition and operation requires an interactive process that needs to be measured constantly. As a result, to ensure continuous success, make sure to test the process before fully implementing the process or subprocesses and tasks. Proper testing will help you spot bugs, identify discrepancies and mistakes, and find any issues or oversights in your process definition.
Testing each step in the process before deploying at scale is critically important to give managers and stakeholders a chance to practice the new process in full. Once you have done thorough quality assurance testing and fixed any issues or problems, you are ready to widely implement your defined business process.
7. Measure business value
A good business process delivers value. Creating and testing the tasks and activities of a process are important. But without creating ways to measure success, you can quickly find yourself involved in inefficient, ineffective, or unnecessary tasks and processes.
Use the process goals you set out in planning and measure how well your new business process is meeting them. The use of process management tools and solutions can help you and your managers track process performance, process mapping and execution progress; assist with future iterations; and determine if your goals are being met.
8. Gather feedback for continuous process improvement
The key to continuously well-performing processes goes beyond simply measuring and testing to getting end-user feedback and finding opportunities for continued improvement. Gather feedback from your stakeholders on how the new process is working for them. Check on those value measures set at the beginning to see if your new process is an improvement and driving success. By continuously monitoring your process performance, you can continually improve, optimize and streamline your process.
Be successful by taking a multistep approach to business processes
Mapping out your business processes from start to finish, with business goals uppermost in mind, and monitoring them after they are implemented takes effort and time. Fortunately, there are well-established methods to identify the key steps to ensure business processes function effectively and return the desired returns. There are also an increasing number of business process management tools, some powered by AI, that can identify and optimize business processes. Using the steps above as a guide can ensure your organization's product or service continues delivering high-quality value to customers and stakeholders.




