
Getty Images/iStockphoto
How to make a successful e-commerce website
E-commerce sites can offer a high ROI because they require less investment than physical stores. However, they may fail to generate revenue without proper design and marketing.
Organizations can build e-commerce sites relatively quickly, but for maximum success, they should consider key elements such as page layout, catalog quality and product pricing.
E-commerce websites can reach large audiences and let people shop 24/7 year-round, which can help organizations increase revenue and acquire new customers. Additionally, these sites require less overhead to operate than brick and mortar stores. However, if business leaders don't consider target audience, page design and contact center staffing before they make their e-commerce websites, their sites may fail due to poor CX and customer service.
Why make an e-commerce website?
An e-commerce website can boost an organization's CX because it offers customers the convenience and flexibility to shop from anywhere, anytime. These online stores can use automatic product recommendations to give customers a personalized shopping experience and improve an organization's ability to upsell. Additionally, e-commerce sites can generate a high ROI because they require a small investment compared to physical stores, which demand location rental, utility fees and in-store staff.
8 steps to make an e-commerce website
E-commerce websites can generate significant revenue, but only if organizations follow best practices. To make a successful e-commerce website, business leaders should take the following steps.
1. Consider an e-commerce platform
Organizations no longer need to design an e-commerce website from the top down. In the past, they had to custom code every catalog, payment and shipping page themselves. Now, organizations have the option to integrate their sites with an e-commerce platform.
Several vendors offer platforms that let business professionals customize page designs and integrate them with their organization's domain name. These platforms -- many of which offer straightforward administrative functions -- include the following:
- Shopify
- Square
- BigCommerce
- Wix
- WooCommerce
- Amazon
- eBay
Although many platforms largely target U.S. and European markets, other e-commerce platforms, such as JD.com and Alibaba, offer access to markets in China. Organizations that don't want to invest in web development should consider an e-commerce platform.
2. Design for a target audience and brand identity
Organizations must identify their target audiences so they can create an e-commerce site design that meets customer expectations. For example, a jewelry store's customers likely value fashion and elegance and would enjoy a fashionable and elegant site design as they shop online. Conversely, an outdoor apparel store may want to focus its site design on ruggedness. Customer demographics such as age, gender, income level and geographic location can help organizations understand their audience's design preferences.
Additionally, organizations should match their e-commerce site design with their brand identity to encourage brand recognition. For instance, if a beauty shop uses a pink star as its logo, it may want to consider a pink-themed site design that features the logo in key places. Once organizations identify their target audiences, creative teams can design layouts that resonate with their customers and brand identity.
3. Build a marketing strategy
To maximize site traffic, organizations should market their e-commerce sites on all channels that can reach their target audiences, which may include social media and Google Ads. Additionally, marketing teams should use SEO best practices in their content to reach new search engine users and send email newsletters to stay in contact with existing customers.
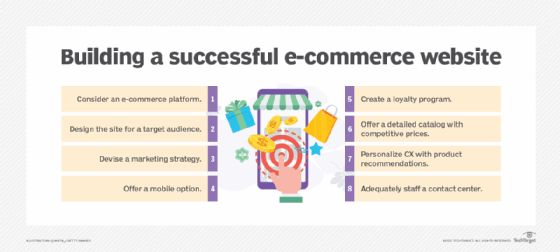
4. Offer a mobile option
Many people use their phones to shop online, so before an organization develops its e-commerce site or chooses a third-party platform, it must ensure that the developers or platform can facilitate a smooth mobile experience. Organizations can also build mobile apps that customers can download for free on iPhone and Android devices. Although mobile app development may cost organizations significantly more than just a mobile-friendly website, these apps can offer customers a more personalized and engaging CX than a website.
5. Create a loyalty program
Loyalty programs reward customers for their repeat business, which can help organizations boost sales on their e-commerce sites. These programs often follow a free model where customers can enroll without charge and gain points as they spend more money with the organization. Other organizations offer a paid subscription model where members pay a fee to join but receive instant benefits. Whether free or subscription-based, loyalty programs can boost customer retention and brand loyalty.
6. Offer a detailed catalog and competitive prices
Online shoppers expect detailed product descriptions, so organizations should offer high-quality images and textual descriptions for all items in their catalogs. Organizations may even consider video descriptions for high-end or complex items. Additionally, web customers can easily discover competitor prices online, so organizations must offer competitive prices on their e-commerce sites.
7. Personalize the shopping experience
Organizations can increase their online sales by personalizing their customers' shopping experiences. For example, organizations can use automatic recommendations on their e-commerce sites to provide personalized product suggestions to customers based on their web activity and purchase history. These recommendations can introduce customers to new and relevant products and increase an organization's sales.
8. Adequately staff a contact center
Although e-commerce can eliminate the need for employees to take orders, process credit cards and send product information, customer service agents must respond to customer inquiries and questions about products and services. For example, organizations must appropriately staff their contact centers so agents can promptly respond to customer emails, phone calls, social media posts and live chat requests.
With third-party e-commerce platforms, organizations can quickly implement an e-commerce website. However, business leaders shouldn't rush the process. Before organizations build their websites, they must consider key elements, such as target audience, design, catalog quality, marketing strategy, mobile functionality and contact center staffing.
If an organization launches an e-commerce site before they have quality item descriptions or appropriately staff their contact center, poor CX and customer service can frustrate customers and hurt the brand. Also, online stores face steep competition, so organizations must price their products appropriately and ensure their sites function smoothly on desktop and mobile devices.




