tablet (tablet PC)
What is a tablet (tablet PC)?
A tablet is a wireless, portable personal computer with a touchscreen interface. The tablet form factor is typically smaller than a notebook computer, but larger than a smartphone.
A tablet PC -- also known as a tablet computer or simply tablet -- is a smaller version of a laptop computer and a larger version of a smartphone. All tablets feature a touchscreen interface, allowing users to engage with the device using touch commands and easily access many applications without needing an external keyboard or mouse.
That said, users can connect an external keyboard or mouse to a tablet. In fact, many users prefer to work with an external input device for gaming, to create documents, access websites and do other tasks on a tablet.
Unlike many laptops, a tablet is a highly portable device, making it easy to carry and transport. And compared to a smartphone, tablets feature a larger form factor and larger screens, thus providing a larger and clearer display experience. Tablets also provide greater storage capacity and a longer battery life compared to smartphones.
Like both laptops and smartphones, tablets are built to work in online and offline modes. Depending on the model and country of operation, tablets are compatible with most wireless and cellular data networks.

Key characteristics of tablet PCs
One of the most important characteristics of tablet PCs is portability. Tablets are smaller and lighter than laptops, making it easy for users to carry them as needed. That said, tablets are too big to be carried in pockets or purses (like smartphones). Also, if the tablet is dropped, its screen can be damaged, so it's advisable to store and carry it in a good quality carrying case.
Viewability is another key characteristic. Since tablets are larger than smartphones, they are more suitable for applications that require higher viewability, including applications involving graphics like games or photo editing. Depending on the application, users can choose 5-inch, 7-inch, 9-inch and 10-inch tablet screen sizes. Larger tablets (13-inch diagonal screen size) are also available.
All tablets feature a capacitive touchscreen interface and offer users various "action" options to access and use applications, such as slide, pinch, etc. In addition, many devices accept input from a pen or stylus, provide a virtual keyboard and can be connected to an external QWERTY keyboard or mouse to enhance usability.
Modern tablets provide multiple connectivity options, meaning they can connect to the internet using WiFi and cellular networks. Web browsing capabilities, web browsers and multimedia applications are also built into tablets.
Finally, tablet PCs can be used in both portrait and landscape mode, depending on the user's requirement and application. The device incorporates an accelerometer with motion-sensing technology that can detect movement and tilt, which allows the screen to automatically rotate and change its mode to match the user's needs.

What are the types of tablets?
Today, the most common type of tablet is the slate style, like Apple's iPad, Microsoft's Surface or Amazon's Fire. External keyboards are available for most slate-style tablets, and some keyboards also function as docking stations for the devices.
Other styles of tablets include the following:
Convertible tablets
These typically have a display that rotates 180 degrees and can be folded to close, screen facing up, over an integrated hardware keyboard. Convertible models may allow user input through a variety of methods in addition to the hardware keyboard, including natural handwriting with a stylus or digital pen, or through a screen-based software keyboard.
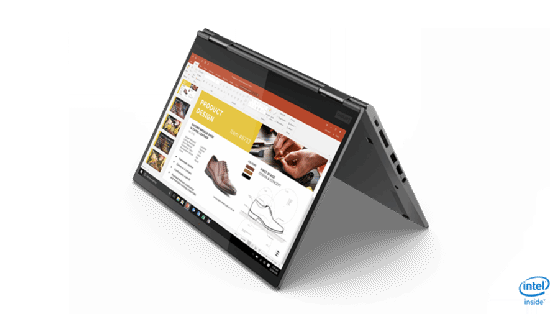
Hybrid tablets
Sometimes referred to as a convertible notebook, a hybrid notebook or a 2-in-1 laptop, a hybrid tablet is like a regular notebook, but has a removable display that functions independently as a slate. The device can be used as both a laptop and a tablet since it offers the features of the former and the convenience and portability of the latter.
Rugged tablets
A slate-like model that is designed to withstand rough handling and extreme conditions, a rugged tablet is usually encased in a thick protective shell and has a shock-protected hard drive. Rugged tablets are commonly used in manufacturing facilities, oil rigs, mines, construction sites, military operations and any other environment characterized by harsh conditions like chemical spills, extreme temperatures, shocks, vibrations, dust, humidity and water exposure.
History and evolution of tablets
The idea of tablet computing is generally credited to Alan Kay of Xerox, who sketched out the idea of a Dynabook in the late 1960s and early 1970s. However, the Dynabook was never actually built and the original predecessor of the tablet PC was the RAND Tablet. This device was developed in the 1960s and included a handwriting recognition program called GRAIL that allowed users to input text and shapes into a larger computer.
In 1987, two companies introduced tablet computers: Cambridge Computer (Z88) and Linus Technologies (Write-Top). The Z88 included an internal floppy drive, accepted input through a keyboard, and was more portable than the Write-Top. The Write-Top accepted input through a stylus, making it one of the first computing devices to do so.
The first widely sold tablet computer was Apple Computer's Newton, which was first shipped in 1993 and touted as a personal digital assistant. The Newton was not a commercial success and Apple discontinued it in 1998.
Since those early days, technological advances in battery life, display resolution, handwriting recognition software, memory and wireless internet access have made tablets a viable computing option. Today, consumers and businesses have a range of tablet devices and operating systems to choose from. Collectively, tablets have made numerous technological advances and gained increasing popularity in enterprise BYOD environments.
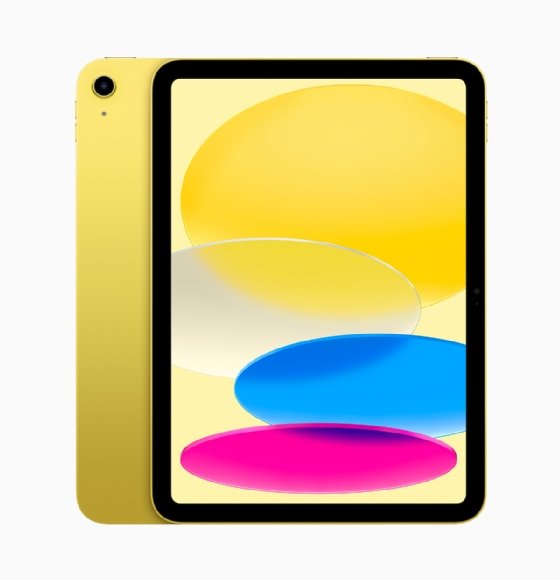

Apple is largely responsible for igniting tablets' current popularity, having released its first-generation iPad in April 2010. Since then, Apple has developed a family of associated devices, including the iPad Air, iPad Pro and iPad Mini.
In addition to Apple, many other computer companies manufacturer and sell tablets, including the following: Lenovo., Microsoft., Samsung. Asus, Acer, Google, Dell and HP.
Find out more about the advantages and disadvantages of mobile devices in business. See how to implement tablets for enterprise use and check out this ultimate guide to mobile device security in the workplace.




