
cloud telephony (cloud calling)
What is cloud telephony (cloud calling)?
Cloud telephony (cloud calling) is a type of unified communications as a service (UCaaS) that offers voice communication services through a third-party host. UCaaS replaces the need for conventional enterprise telephone systems, such as private branch exchange (PBX). Cloud telephony services can be web- or applications-based.
Cloud communications providers build, operate and maintain standardized telephony platform offerings on their servers, with customers gaining remote access -- via the internet -- on a subscription or as-needed basis. This model lets organizations ditch their conventional, on-premises telephone systems -- such as PBX -- which tend to be relatively expensive and time-consuming to provision and maintain.
While somewhat fluid, the term cloud telephony typically denotes a multi-tenant access model, with subscribers paying to use a provider's pool of commoditized, shared resources. In contrast, hosted telephony usually refers to a dedicated, segregated environment -- essentially, an off-site PBX -- that a major carrier builds, houses and maintains in its cloud for a single organization's use.
How does cloud telephony work?
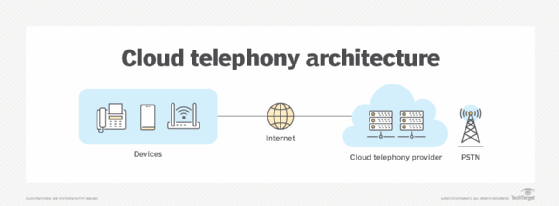
Cloud telephony operates through a voice over IP (VoIP) service provider. Similar to any other VoIP service, it works by converting analog voice signals into digital data packets, which are then delivered through the internet. In cloud telephony, whenever a user makes a phone call using a VoIP desk phone or softphone, the VoIP service provider handles the call routing.
To use this technology, individual phone extensions are replaced by VoIP desk phones, which are connected to the existing network instead of a landline. Alternatively, an organization can use softphones, which are applications installed on computers, tablets or smartphones.
By enabling users to place calls directly from any computer or mobile device with an internet connection, cloud telephony frees up businesses from the burden of buying and storing expensive standalone hardware, such as traditional PBX boxes and handsets.
Benefits of cloud calling
Cloud telephony can provide numerous benefits to businesses, such as saving money on communication expenses, consolidating multiple tools and services, and providing an enhanced customer experience. It's no surprise that cloud telephony is seeing extensive adoption, with the VoIP market anticipated to grow to $327.5 billion by 2031. The following are some of these benefits:
- Cost-effective. Compared with traditional, on-premises options, proponents of cloud telephony say it's more economical. By offloading hosting and management responsibilities to a cloud communications provider that offers subscription and pay-per-use models, which enable resource pooling, organizations can reduce their infrastructure overhead costs.
- Flexible. An employee with a cloud-based telephone number can take and make inbound and outbound calls anywhere with an internet connection, enabling more seamless mobile work.
- Resilient. While a natural disaster, fire or another emergency event can take down an on-site PBX system, cloud calling services tend to offer more resilient service and reliable business continuity. Most cloud telephony services have built-in failover modes that ensure a backup is available if a problem occurs with a connection.
- Scalable. Organizations can typically add or change employee telephone numbers on demand via a self-service portal, enabling efficient employee onboarding and offboarding for both on-site and remote workers.
- Streamlined. With cloud calling, organizations aren't burdened with setting up, maintaining, troubleshooting and updating on-site systems. Instead, third-party providers handle infrastructural upkeep and upgrades.
- Transparent. Many UCaaS platforms provide rich data analytics, offering information about user behavior and insight into optimizing employee efficiency.
- Manageable. Because the entire system is managed in the cloud, IT teams can easily supervise and administer system modifications and edits through an online dashboard, giving them complete control over the company's phone numbers, extensions and call forwarding.
With cloud-based voice technology, organizations can also add advanced features, such as voice and keyword analysis, call center capabilities, interactive voice response and artificial intelligence-enabled customer support. On the other hand, UCaaS analysts say organizations can't yet customize cloud calling offerings to the extent that's possible with on-premises systems, leading many large enterprises to delay adoption.
Risks of cloud calling
Along with its many benefits, cloud telephony also comes with the following drawbacks:
- Internet dependency. Cloud phone systems are dependent on the internet to function. While this has its benefits, a spotty internet connection that drops frequently can lead to communication disruptions. Therefore, a reliable internet signal is crucial for the successful operation of a cloud-based phone system.
- Security concerns. According to experts, cloud telephony platforms can't satisfy some security requirements, with multi-tenant, public cloud environments failing to meet certain stringent compliance regulations. For this reason, organizations dealing with highly sensitive data might opt for on-premises or hosted telephony, where they can ensure resources remain physically segregated and secure.
- Increased hardware cost. Cloud-based phone systems usually require high-performance networking hardware, such as routers and switches, to function. These devices provide specialized capabilities, including network segmentation, traffic shaping and IP address assignment, for an effective VoIP deployment. However, if the infrastructure consists of antiquated routers that can't meet the needs of advanced VoIP deployments, the cost of setting up a cloud telephony system could rise. Also, if a company already has a traditional phone infrastructure in place, converting it into a cloud-enabled system or purchasing new VoIP phones might result in additional expenses.
Cloud telephony vs. VoIP
Virtually all cloud telephony platforms use VoIP technology, but not all VoIP systems run in the cloud. The term VoIP simply indicates how calling data travels over the internet via IP packet-switched connections, rather than over a traditional public switched telephone network.
An enterprise can choose to house its VoIP system on-site or outsource it to a third-party provider. Some organizations create hybrid VoIP environments that use both cloud-based and on-premises calling technology, often as part of a long-term cloud migration strategy.
While cloud telephony includes VoIP as a fundamental component, it goes beyond voice calls and adds functionalities such as advanced call management and scalability.
Cloud telephony providers
Most cloud telephony providers offer a wide range of services and pricing options to accommodate different business needs and organizational sizes. Besides cloud calling services, most vendors provide complementary UCaaS features, such as web conferencing, screen sharing, team messaging and persistent workspaces.
UC analysts expect to see increasingly sophisticated integrations between cloud telephony platforms and other business apps, such as Salesforce and Microsoft 365.
Cloud telephony vendor offerings include the following:
- 8x8. With features such as call handling, conferencing, auto-attendant, Short Message Service (SMS), team messaging and voicemail services with transcription, the 8x8 basic package is designed for small businesses. An upgrade option for larger organizations includes a bundle with single sign-on, integrations with Okta, unlimited faxes and phone recording.
- Cisco Webex Calling. This cloud telephony system caters to midsize businesses, enabling users to make and receive calls across any Cisco IP device, regardless of their location. Cisco Webex also offers end-to-end encryption for calls.
- Dialpad. Dialpad offers teams AI voice technology to optimize call volumes and customer services, along with advanced phone features, such as SMS, instant messaging and video conferencing.
- Google Voice. Google Voice simplifies communication by consolidating telephone numbers, enabling users to receive calls on all their devices, exchange messages, and send and receive voicemails. Available on both iOS and Android platforms, the app is designed for users who want the convenience of having a single number ring on multiple devices simultaneously.
- MagicJack. Established in 2007, this provider offers services similar to a traditional home phone. But, instead of relying on a physical phone line, MagicJack uses an internet connection. Over time, the service has evolved to enable users to make calls while traveling and even receive home phone calls on their smartphones.
- Nextiva. Designed for small to midsize teams of remote, in-house and hybrid workers, Nextiva provides an all-in-one communications service.
- RingCentral. Businesses of all sizes can use the video, text and chat services -- all with the security of an enterprise-grade encrypted phone system.
- Vonage. Vonage Business Communications is designed for organizations that require essential communication channels, such as voice, team chat, SMS and video, but not additional features, such as routing or queueing.
Understanding the differences between a VoIP gateway and PBX is crucial when selecting a phone system that meets the unique needs and requirements of a business. Learn how these systems handle voice data packets and how they differ from each other.



